The (x-a)(x-b) formula can be derived in geometrical approach by splitting a square as three different rectangles. Let’s start deriving the expansion of special product of binomials $x-a$ and $x-b$ in algebraic form.

Take, a square and it is taken that the length of each side is $x$. Now, evaluate the area of a square mathematically.
$Area$ $\,=\,$ $x \times x$
$\implies$ $Area$ $\,=\,$ $x^2$
Therefore, the area of this square is equal to $x^2$ mathematically and remember this.
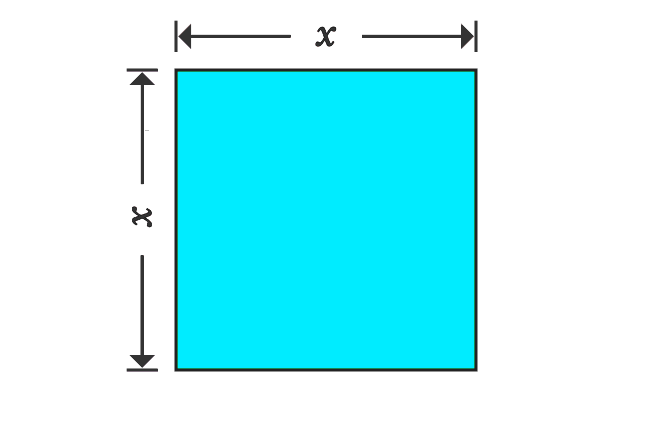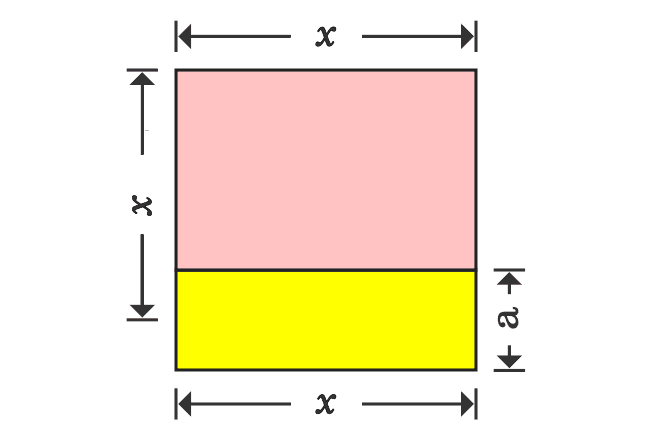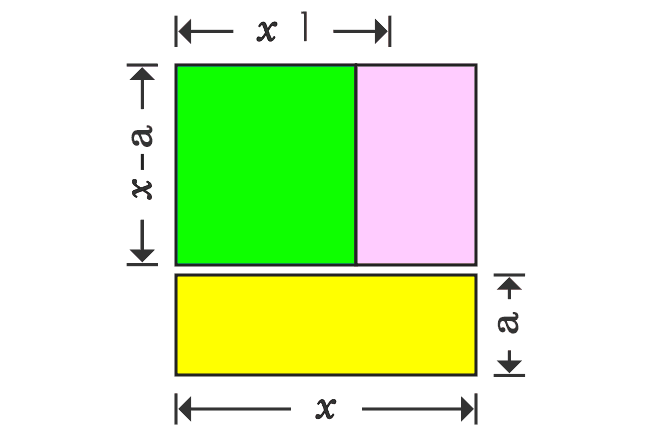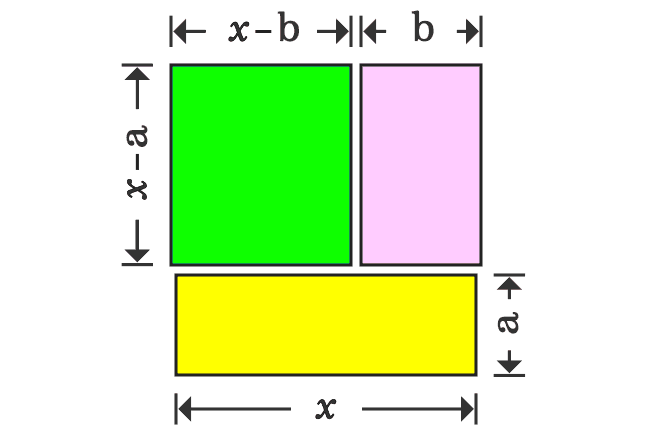
Thus, a square whose area is $x^2$, is split as three different rectangles. Now, write the area of each rectangle in mathematical form.
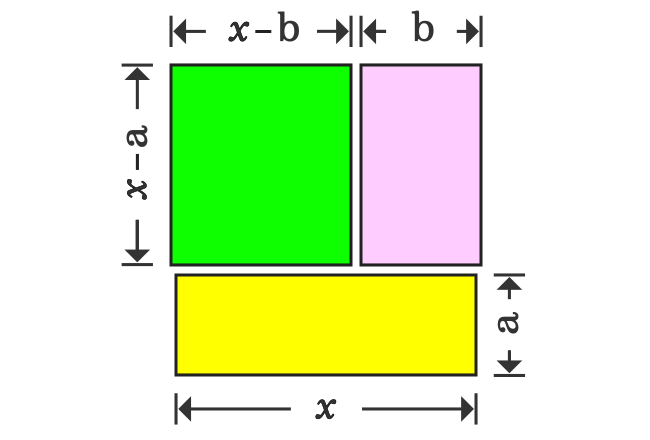
This information is used to derive the expansion for the special product of polynomials $(x-a)(x-b)$ geometrically.
The square whose area is $x^2$, is divided as three different rectangles geometrically. Therefore, the area of a square is equal to sum of the areas of the rectangles.
$x^2$ $\,=\,$ $(x-b)(x-a)$ $+$ $b(x-a)$ $+$ $ax$
$\implies$ $x^2$ $\,=\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $+$ $b(x-a)$ $+$ $ax$
$\implies$ $x^2$ $\,=\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $+$ $bx-ba$ $+$ $ax$
$\implies$ $x^2$ $\,=\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $+$ $ax+bx$ $-$ $ba$
$\implies$ $x^2$ $\,=\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $+$ $ax+bx$ $-$ $ab$
$\implies$ $x^2$ $\,=\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $+$ $(a+b)x$ $-$ $ab$
$\implies$ $x^2$ $-$ $(a+b)x$ $+$ $ab$ $\,=\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $\,=\,$ $x^2$ $-$ $(a+b)x$ $+$ $ab$
Therefore, it is proved that the product of special binomials $x-a$ and $x-b$ is equal to the algebraic expression $x^2-(a+b)x+ab$.
This algebraic identity can also be derived directly in alternative method in geometry. The rectangle whose area is $(x-b)(x-a)$ can be obtained by subtracting the rectangles whose areas are $b(x-a)$ and $ax$ from the square whose area is $x^2$.
$(x-a)(x-b)$ $\,=\,$ $x^2$ $-$ $\Big(b(x-a)+ax\Big)$
$\implies$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $\,=\,$ $x^2$ $-$ $\Big(bx-ba+ax\Big)$
$\implies$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $\,=\,$ $x^2$ $-$ $\Big(ax+bx-ab\Big)$
$\implies$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $\,=\,$ $x^2$ $-$ $\Big((a+b)x-ab\Big)$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $(x-a)(x-b)$ $\,=\,$ $x^2-(a+b)x+ab$
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved