A number line that displayed in vertical position in a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system is called the $y$-axis of two dimensional space.
In Bi-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, there are two number-lines, which are bisected at their middle point but one of them is drawn vertically for measuring the distance of a point from origin in vertical direction. Therefore, the number-line is called the $y$-axis of the two dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.
The $y$-axis is represented by a number-line $YOY’$ in this example. The arrows above and below in number-line $\overleftrightarrow{YY’}$ represents that the straight line can be extended infinitely in both directions.
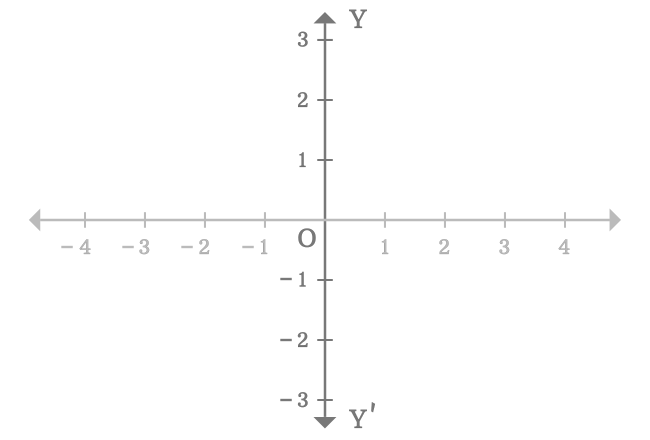
In two-dimensional space, the horizontal number-line divides the $y$-axis as two parts at origin $(O)$.
The part of the $y$-axis that appears above the origin is called the positive $y$-axis. In this case, the ray $\overrightarrow{OY}$ represents the positive $y$-axis. Every division in the positive $y$-axis is denoted by the positive integers.
The part of the $y$-axis that appears below the origin is called the negative $y$-axis. In this case, the ray $\overrightarrow{OY’}$ denotes the negative $y$-axis. Each division in the negative $y$-axis is represented by the negative integers.
In two-dimensional space, the $y$-axis is used to know the distance of any point from the origin by comparing the vertical distance of the point with the number line on the $y$-axis. For example, $E$, $F$, $G$ and $H$ are four points in a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.
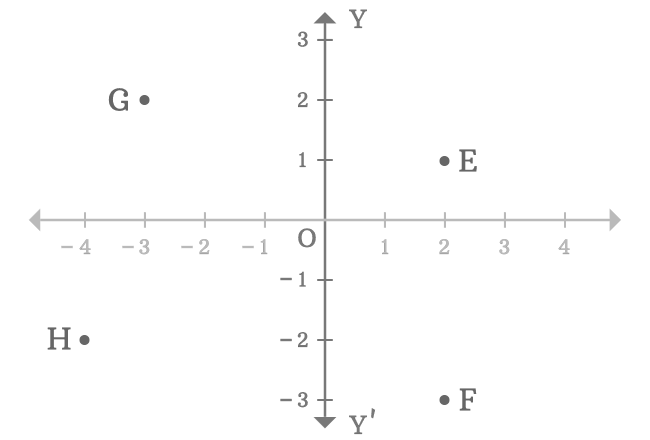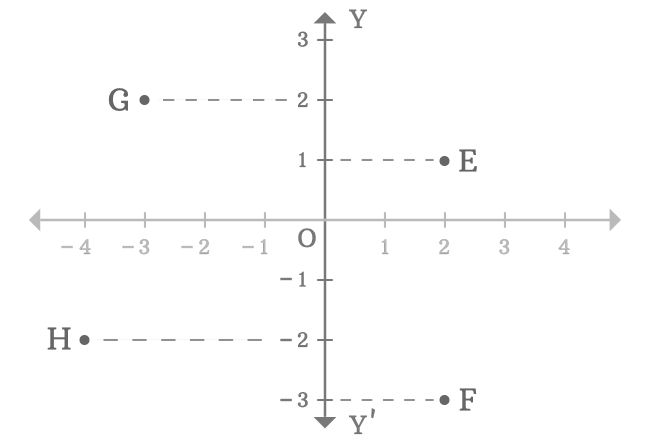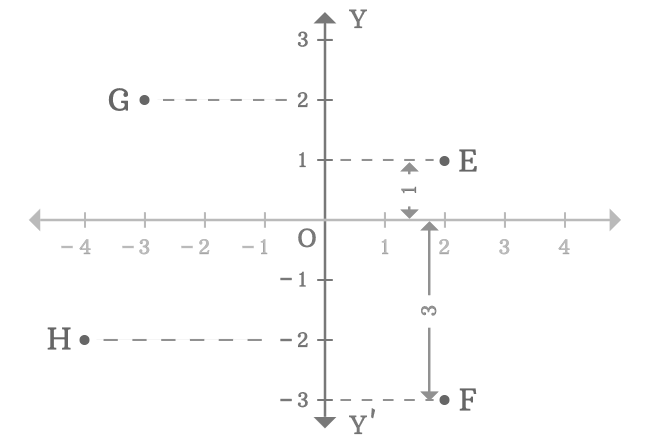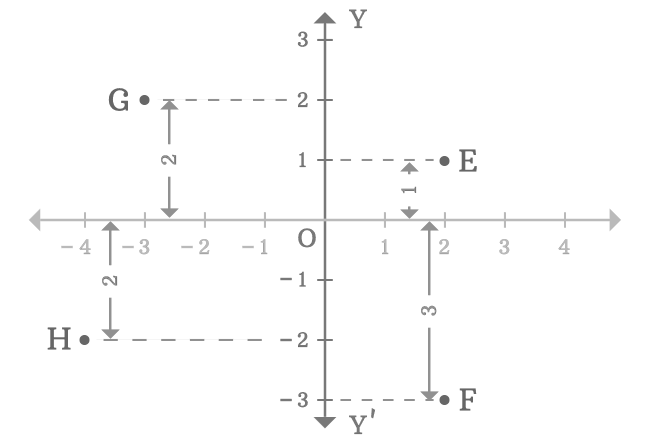
In this way, the $y$-axis is used to measure the distance of any point from the origin in vertical direction by the comparison.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2023 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved