The left-bottom side region in the two dimensional space is called the third quadrant.
Two number lines are perpendicularly bisected at their middle point in bi-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system for splitting the coordinate plane into four equal regions.
The left-bottom side region is called the third quadrant. In this case, the region in the angle $X’OY’$ is the third quadrant and represented by a Roman numeral $III$.
In $\angle X’OY’$, the $x$-axis and $y$-axis both represent negative values. Therefore, the abscissa and ordinate of every point in this region should be negative.
If $x$-coordinate and $y$-coordinate of each point are denoted by $x$ and $y$ respectively, then the values of both coordinates are written in mathematical form as $x < 0$ and $y < 0$.
The third quadrant is used in the bi dimensional space to identity the location of a point whose abscissa and ordinate are negative. So, let’s study how to use the third quadrant in coordinate geometry.
Identify the location of the point $C(-6, -4)$.
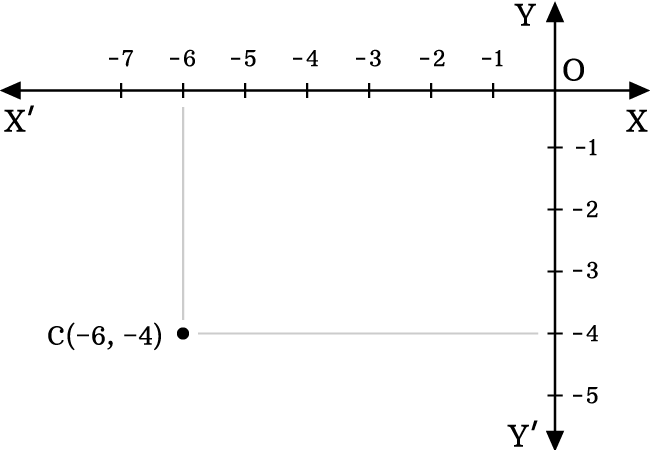
Here, the $x$ coordinate (or abscissa) is $-6$ and $y$ coordinate (or ordinate) is $-4$.
In this way, the third quadrant of two dimensional Cartesian coordinate system is used for identifying the location of any point whose both abscissa and ordinate are negative.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved