Mathematically, the exact value of cot of $45$ degrees can be derived in three different methods. One of three methods is trigonometric approach but the remaining two methods are slightly different geometric methods. Study all of them here to know how to find the $\cot{(50^g)}$ value in trigonometry.
On the basis of direct relation between adjacent and opposite sides, the value of $\cot{\Big(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\Big)}$ is derived in mathematics in theoretical geometry method.
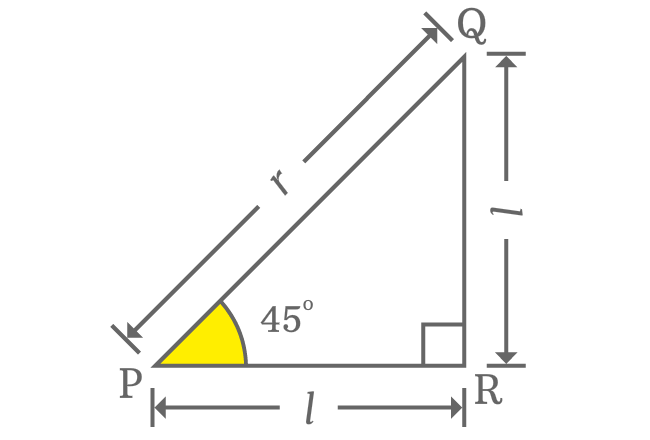
$\cot{(45^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side}{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}$
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{PR}{QR}$
The lengths of adjacent and opposite sides are equal when angle of right triangle is $\dfrac{\pi}{4}$ radians. Therefore, the length of both opposite and adjacent sides is denoted by $l$ in this case.
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{l}{l}$
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \require{cancel} \dfrac{\cancel{l}}{\cancel{l}}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, 1$
You can even find the exact value of cot of $\dfrac{\pi}{4}$ radians on your own by constructing a right triangle with $45$ degrees angle by using geometrical tools. Here, you are going to learn how to find it geometrically.

The $\Delta MKL$ is a right triangle with $45$ degrees angle. Now, let’s find the exact value of $\cot{(50^g)}$ from this triangle.
$\cot{(45^°)} = \dfrac{Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side}{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}$
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{KM}{LM}$
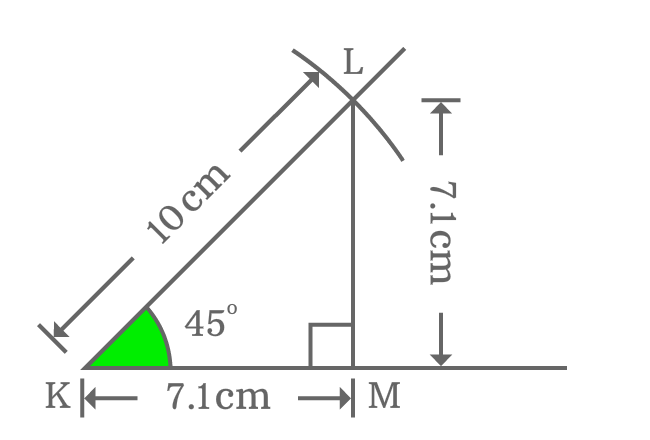
Actually, the lengths of adjacent and opposite sides are unknown but they can be measured by a ruler.
If you measure them by a ruler, you will be understood that the lengths of both adjacent side ($KM$) and opposite side ($LM$) are equal and the length of each side is equal to $7.1 \, cm$ approximately.
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{KM}{LM} = \dfrac{7.1}{7.1}$
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \require{cancel} \dfrac{\cancel{7.1}}{\cancel{7.1}}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, 1$
The value of cotangent of $45$ degrees can be exactly evaluated in trigonometry by the reciprocal identity of tan function.
$\cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{1}{\tan{(45^°)}}$
Now, substitute the value of tan of $45$ degrees to get the $\cot{\Big(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\Big)}$ value.
$\implies \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{1}{1}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \cot{(45^°)} \,=\, 1$
According to proofs of cot of $45$ degrees from above three methods, the exact value of $\cot{\Big(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\Big)}$ is equal to one.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved