The expansion of the algebraic identity a plus b whole square can be derived in mathematical form by the geometrical approach. In this method, the concept of the areas of the geometrical shapes squares and rectangles are used in proving the a plus b whole square formula.
In this step, we evaluate the area of a square in algebraic form.

This geometrical procedure splits a square as four geometric shapes, in which two of them are different squares and remaining two are two rectangles. Now, evaluate the area of each geometrical shape in mathematical form.
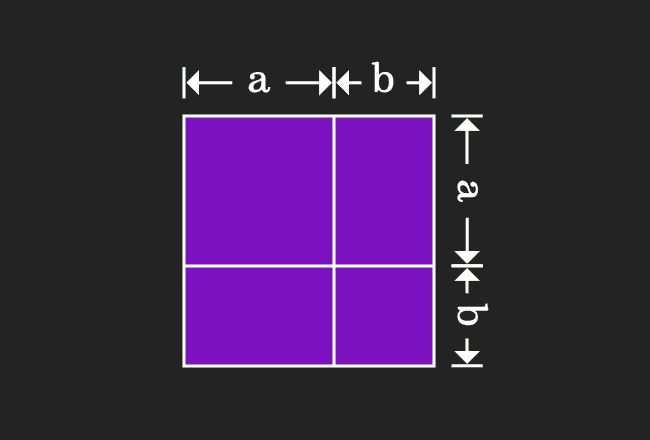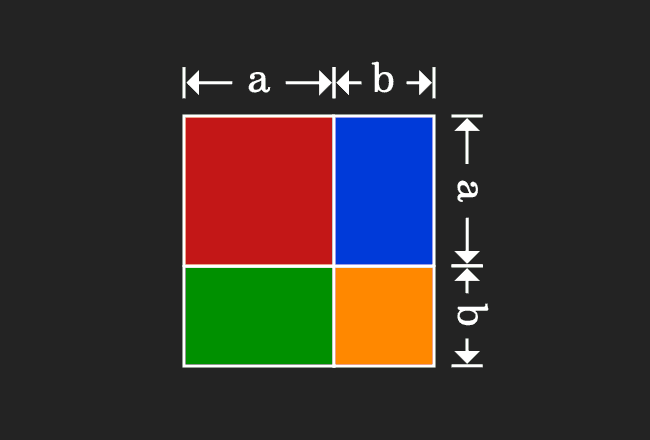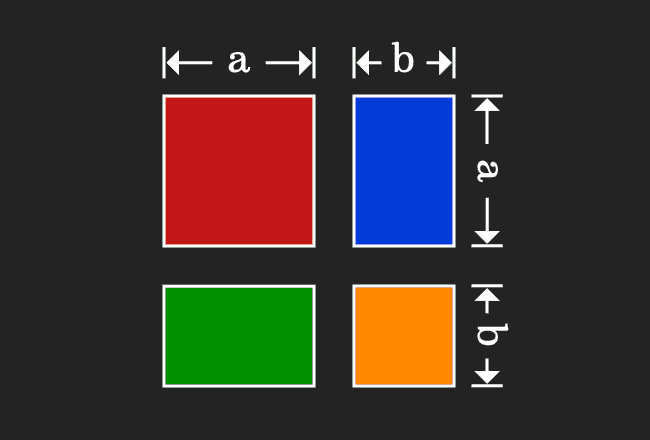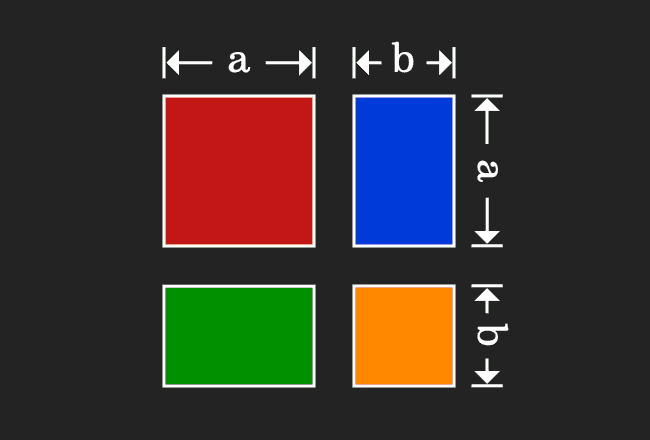
Now, add areas of the all four geometrical shapes to express the whole area in mathematical form.
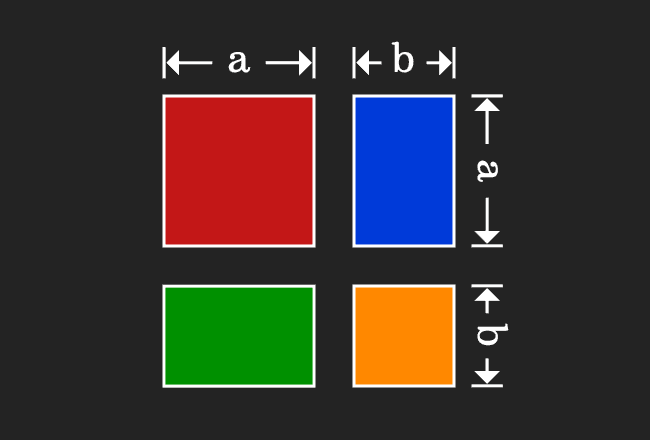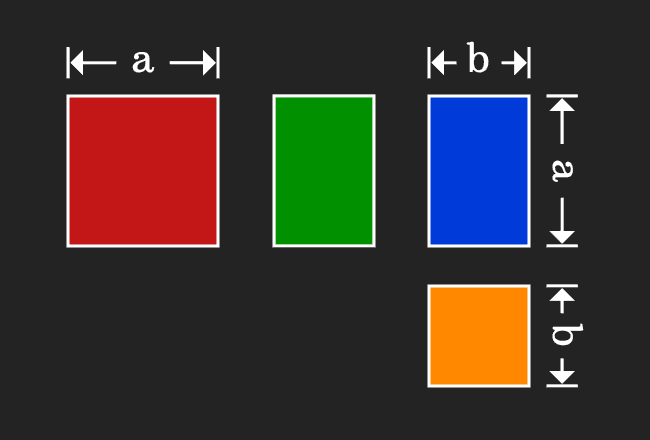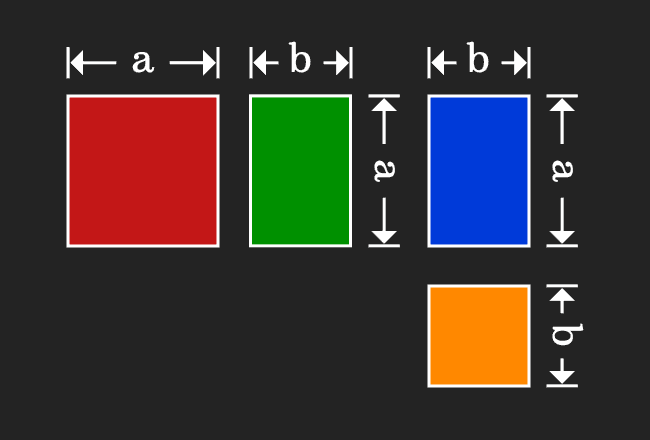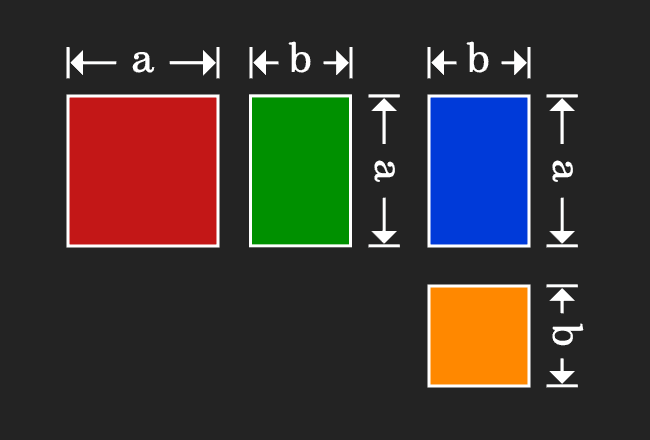
$a^2+ba+ab+b^2$
According to the commutative property of multiplication, the product of $a$ and $b$ is equal to the product of $b$ and $a$. The equality of the areas of both rectangles can also be proved geometrically.
Therefore, the term $ba$ can be written as $ab$ and vice-versa.
$\implies$ $a^2+ab+ab+b^2$
$\implies$ $a^2+2ab+b^2$
$\implies$ $a^2+b^2+2ab$
We are going to learn the equality property in the mathematical form.
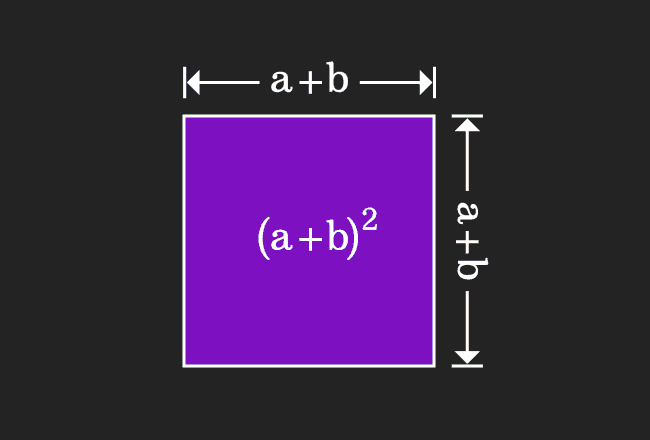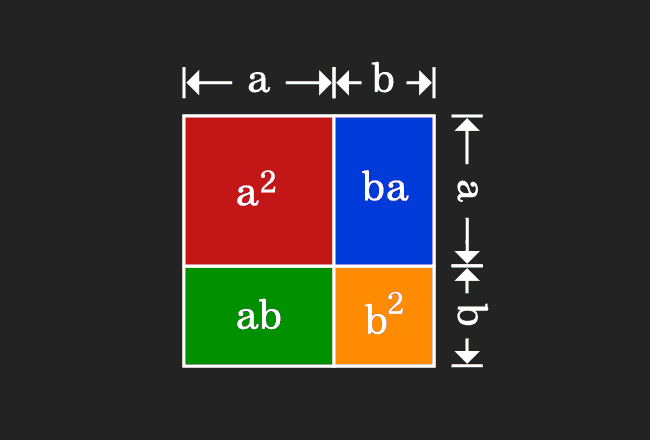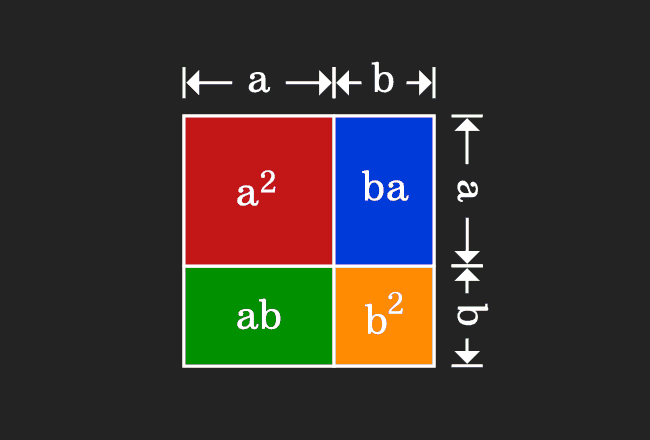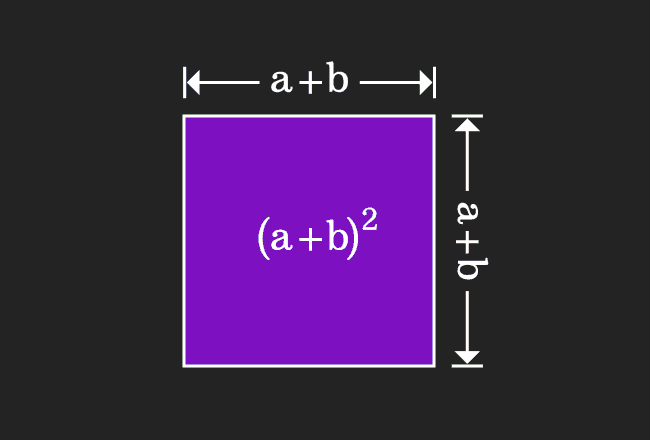
Actually, a square is divided as four geometrical shapes. It is obvious that the area of the square is equal to sum of the areas of them.
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ ${(a+b)}^2$ $\,=\,$ $a^2 + b^2 + 2ab$
Geometrically, it is proved that square of $a+b$ can be expanded as $a$ squared plus $b$ squared plus two times product of $a$ and $b$.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved