The distance of an intersecting point of a straight line and horizontal axis from origin is called $x$-intercept.
A straight line often intersects horizontal x-axis at a point. The distance from the intersecting point from origin in x-axis direction is known as $x$-intercept.
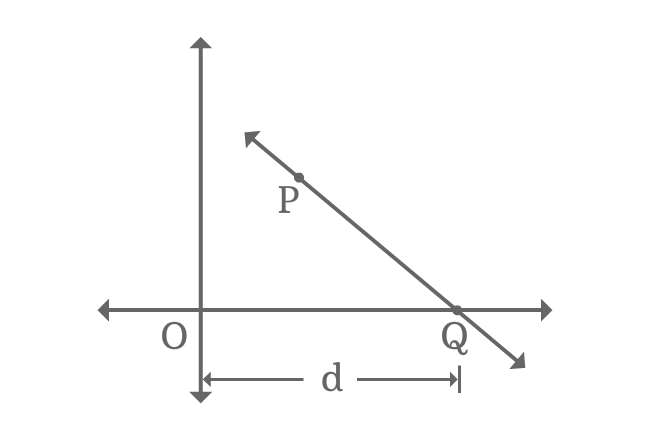
Imagine a straight line in Cartesian coordinate system. It intersects the horizontal $x$-axis at point $Q$ and $P$ is a point on the straight line.
The distance from origin to intersecting point of straight line $\overleftrightarrow{PQ}$ and $x$-axis in horizontal axis direction is $d$. The distance $d$ is called $x$-intercept.
$x$-intercept $\,=\,$ $d$
$\implies OQ$ $\,=\,$ $d$
The intersecting point $Q$ is on $x$-axis. So, its $y$-coordinate is equal to zero but its $x$-coordinate is equal to $x$-intercept. Therefore, the intersecting point $Q$ in the form of coordinates is $(d, 0)$.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2023 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved