Proof of $\sin{(30^°)}$ in Theoretical Geometric method
Fact-checked:
There is a special geometrical relation between opposite side and hypotenuse when angle of right triangle is $30$ degrees and this property is used to derive the exact value of $\sin{30^°}$ in fraction and decimal form mathematically.
Theoretically, the length of opposite side is always half of the length of hypotenuse when angle of right triangle is $30$ degrees.
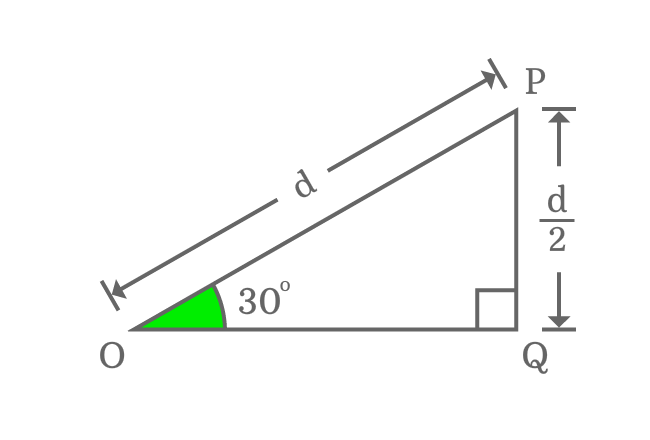
In $\Delta POQ$, the length of hypotenuse is taken as $d$. So, the length of the opposite side should be half of it. Hence, the length of opposite side is $\dfrac{d}{2}$.
Calculate the ratio of length of opposite side to length of hypotenuse.
$\dfrac{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{PQ}{OP}$
$\implies$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{\dfrac{d}{2}}{d}$
$\implies$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{d}{2 \times d}$
$\implies$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$ $\,=\,$ $\require{cancel} \dfrac{\cancel{d}}{2 \times \cancel{d}}$
$\implies$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{1}{2 \times 1}$
$\implies$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{1}{2}$
The ratio of lengths of opposite side to hypotenuse is called sine in trigonometry and the ratio between them is calculated when angle of right triangle $POQ$ is $30^°$. Trigonometrically, the ratio of lengths of opposite side to hypotenuse when angle of right triangle equals to $30^°$ is called sin of angle $30$ degrees.
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $\sin{(30^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{1}{2}$
It is exact value of sin $30$ degrees in fraction form and it can be written in decimal as well.
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $\sin{(30^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $0.5$
Thus, the value of sine of angle $30$ degrees is derived theoretically in geometrical system.

