Pythagorean Theorem
The square of length of hypotenuse equals to the sum of squares of opposite and adjacent sides of a right triangle is called the Pythagorean Theorem.
Introduction
A Greek Mathematician Pythagoras identified the direct geometrical relationship between the sides of a right triangle.
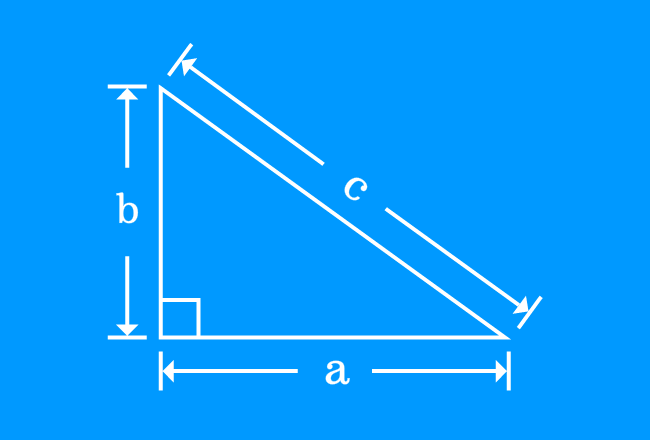
He observed that the square of length of hypotenuse of a right triangle is exactly equal to the sum of squares of lengths of opposite and adjacent sides of the same triangle.
Example
If $a$, $b$ and $c$ are lengths of opposite side, adjacent side and hypotenuse of a right triangle, then direct relation between them can be expressed in mathematical form as follows.
$\large c^2 \,=\, a^2+b^2$
Proof
Learn how to derive the Pythagorean theorem in algebraic form by the geometrical system.
