$m \,=\, \tan{\theta}$
The tangent of inclination of a straight line is called the slope of straight line.
$\overleftrightarrow{PQ}$ is a straight line in Cartesian coordinate system with some inclination.
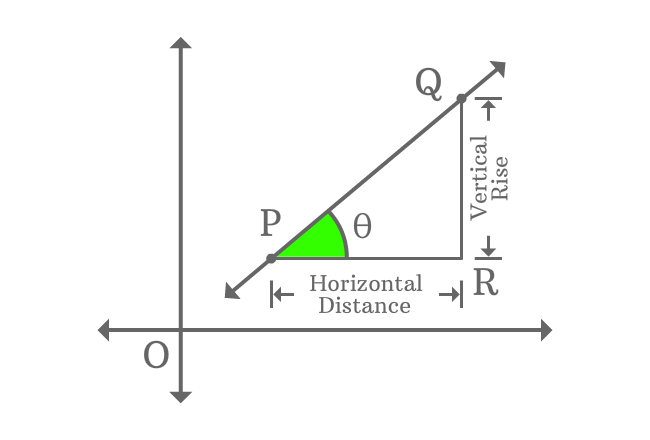
Draw a parallel line to $x$-axis from point $P$ and also draw a perpendicular line towards $x$-axis from point $Q$. The both lines are intersected at point $R$ perpendicularly and it formed a right triangle ($\Delta RPQ$) geometrically.
The lengths of $\overline{QR}$ and $\overline{PR}$ represent vertical rise and horizontal distance of points of $P$ and $Q$ of the straight line. The slope of this straight line is ratio of vertical rise to horizontal distance of points of the straight line.
The slope of straight line $\overleftrightarrow{PQ}$ is represented by letter $m$ mathematically in geometric system.
$m \,=\, \dfrac{Vertical \, Rise}{Horizontal \, Distance}$
$\implies m \,=\, \dfrac{QR}{PR}$
$\Delta RPQ$ is a right triangle and, $\overline{QR}$ and $\overline{PR}$ are opposite side and adjacent side of the right triangle. Theta ($(\theta)$) is inclination of the straight line and it is also angle of the right triangle. The ratio of $QR$ to $PR$ is tan of angle theta as per trigonometry.
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, m \,=\, \tan{\theta}$
The derivation has proved that the slope of a straight line is equal to tangent of the inclination of the straight line.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved