$\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b} \,=\, 1$
It is an equation of a straight line when a straight line intersects both axes with $x$ and $y$ intercepts.
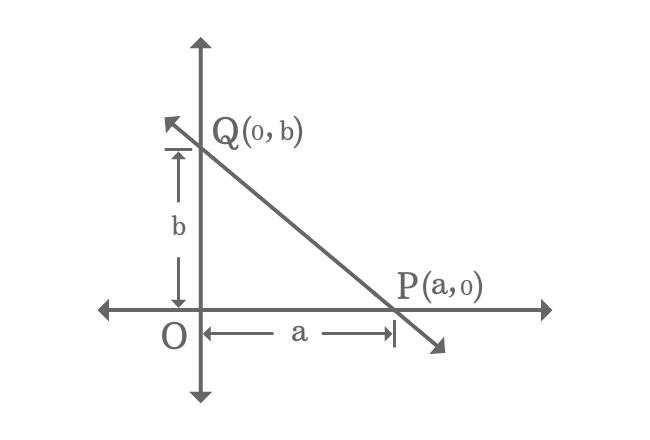
A straight line intersects both horizontal and vertical axes of Cartesian coordinate system at $P$ and $Q$ points with $a$ as $x$-intercept and $b$ as $y$-intercept.
The intersecting points of straight line $\small \overleftrightarrow{PQ}$ in coordinate form are $P(a, 0)$ and $Q(0, b)$.
$A(x, y)$ is any point on the straight line $\small \overleftrightarrow{PQ}$. Draw a perpendicular line to $x$-axis from point $A$ and it intersects the $x$-axis at point $B$.
Similarly, draw a perpendicular line to $y$-axis from point $A$ and it intersects the $y$-axis at point $C$.
It formed two right triangles $\Delta APB$ and $\Delta QAC$. The adjacent side of $\Delta APB$ is on $x$-axis and the adjacent side of $\Delta QAC$ is parallel to the $x$-axis. Similarly, the opposite side of $\Delta QAC$ is on $y$-axis and the opposite side of $\Delta APB$ is parallel to the $y$-axis. The hypotenuse of both right triangles are part of straight line $\small \overleftrightarrow{PQ}$.
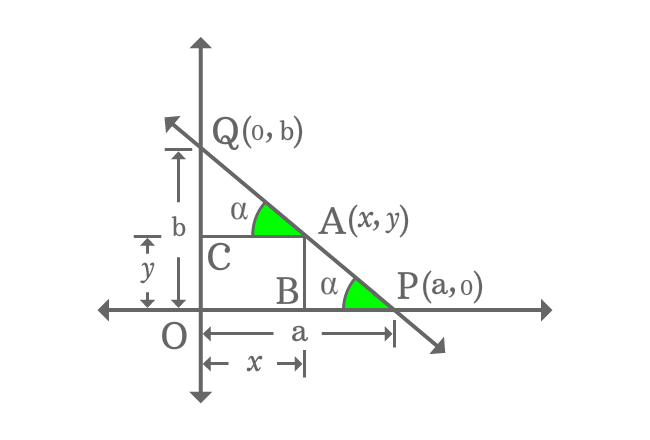
Therefore, the right triangles $\Delta APB$ and $\Delta QAC$ are similar triangles. Hence, the corresponding angles of both triangles are same.
If $\angle QAC$ is equal to $\alpha$, then $\angle APB$ is also equal to $\alpha$.
According to $\Delta APB$
$\tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{AB}{BP}$
$\implies \tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{AB}{OP-OB}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{y}{a-x}$
According to $\Delta QAC$
$\tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{QC}{AC}$
$\implies \tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{OQ-OC}{AC}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{b-y}{x}$
According to both $\Delta APB$ and $\Delta QAC$
$\tan{\alpha} \,=\, \dfrac{y}{a-x} \,=\, \dfrac{b-y}{x}$
Now, simplify the equation to get the equation of a straight line in intercept form.
$\dfrac{y}{a-x} \,=\, \dfrac{b-y}{x}$
$\implies xy \,=\, (a-x)(b-y)$
$\implies xy \,=\, a(b-y)-x(b-y)$
$\implies xy \,=\, ab-ay-xb+xy$
$\implies \require{cancel} \cancel{xy} \,=\, ab-ay-xb+\cancel{xy}$
$\implies 0 \,=\, ab-ay-xb$
$\implies bx+ay \,=\, ab$
$\implies \dfrac{bx+ay}{ab} \,=\, 1$
$\implies \dfrac{bx}{ab}+\dfrac{ay}{ab} \,=\, 1$
$\implies \require{cancel} \dfrac{\cancel{b}x}{a\cancel{b}}+\dfrac{\cancel{a}y}{\cancel{a}b} \,=\, 1$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b} \,=\, 1$
It is a linear equation in algebraic form and represents an equation of straight line when a straight line intersects both axes with double intercept.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved