Expand $(3x − 5y)^2$
The expression $3x-5y$ is a binomial involving the variables $x$ and $y$. When this binomial is squared, written as $(3x-5y)^2$, it simply means that the expression $3x-5y$ is multiplied by itself. In this algebra problem, we are asked to expand the expression $3x-5y$ squared.
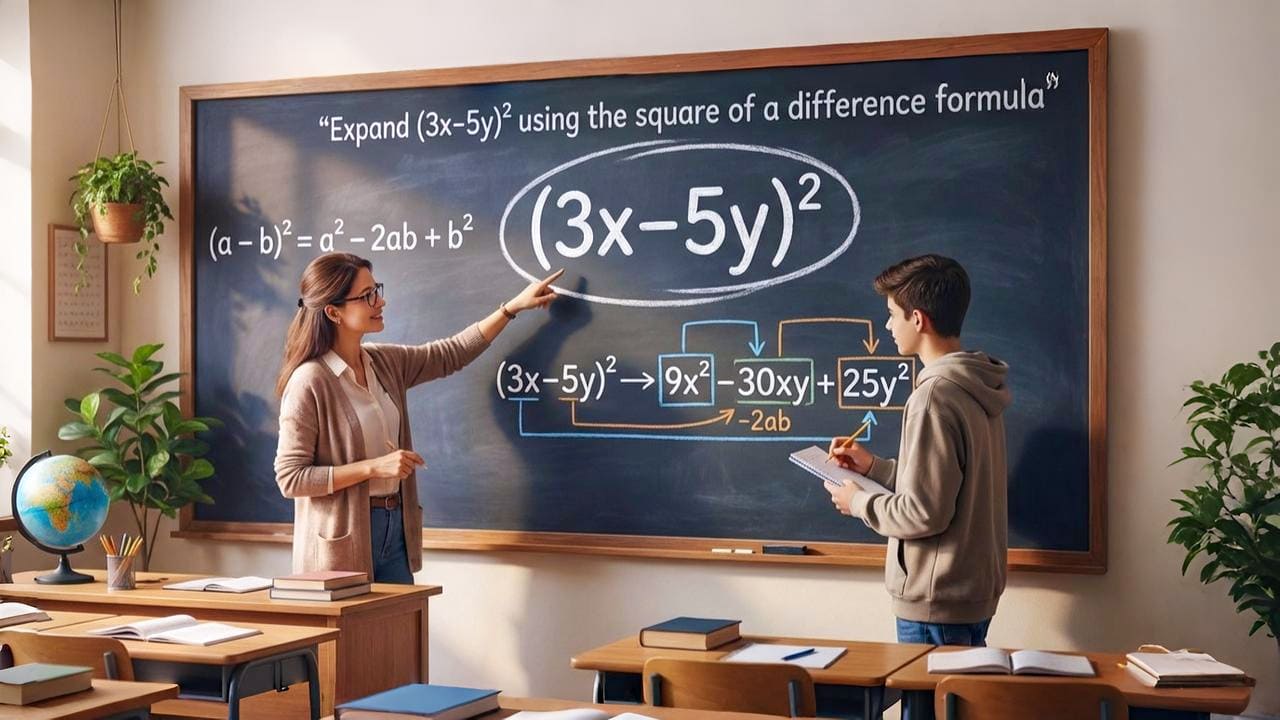
The given algebraic expression $(3x-5y)^2$ represents the square of a difference. Therefore, it can be expanded using the standard formula for the square of a difference.
In this step-by-step explanation, you will learn how to expand $3x-5y$ squared clearly and correctly using the standard algebraic identities.
Identify the Terms in the Algebraic Expression
Expanding a square of a difference expression, like $(3x-5y)^2$, is simple when we use the $a-b$ whole square algebraic identity. To make it easier, let’s assign $a \,=\, 3x$ and $b \,=\, 5y$, to clearly identify the terms.
$\implies$ $(a-b)^2$ $\,=\,$ $(3x − 5y)^2$
Substitute into the Formula to Expand the Expression
Now, let us write the a minus b squared formula and apply it to the given expression.
$(a-b)^2$ $\,=\,$ $a^2-2ab+b^2$
In this step, substitute the values $a \,=\, 3x$ and $b \,=\, 5y$ into the square of a difference formula.
$\implies$ $(3x − 5y)^2$ $\,=\,$ $(3x)^2$ $-$ $2(3x)(5y)$ $+$ $(5y)^2$
Replacing each variable with its corresponding term allows the expression $3x-5y$ whole square to be expanded correctly and systematically. This step is important because it ensures that each term is squared properly and that the middle term has the correct sign.
Simplify the Terms to Complete the Expansion
Now, let us square the first and last terms, and evaluate the middle term carefully to obtain the binomial expansion of $3x-5y$ squared.
$=\,\,$ $3x \times 3x$ $-$ $2 \times 3x \times 5y$ $+$ $5y \times 5y$
$=\,\,$ $9x^2$ $-$ $30xy$ $+$ $25y^2$
Therefore, it is evaluated that the square $3x$ minus $5y$ is equal to $9x$ square minus $30$ $x$ $y$ plus $25y$ square.
$\,\,\,\,\therefore\,\,\,\,$ $(3x − 5y)^2$ $\,=\,$ $9x^2$ $-$ $30xy$ $+$ $25y^2$

