Geometric Proof of Distance formula
Formula
$d = \sqrt{{(x_{2}-x_{1})}^2+{(y_{2}-y_{1})}^2}$
It is a distance formula and used to find the distance between any two points in a two dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. Now, learn how to derive the distance formula in geometry.
Construct a figure to derive distance formula
- $P{(x_{1}, y_{1})}$ and $Q{(x_{2}, y_{2})}$ are two points in two dimensional space.
- Join the points by a line and it forms a line segment $\small \overline{PQ}$. The length of line segment is equal to the distance between the points $P$ and $Q$ geometrically.
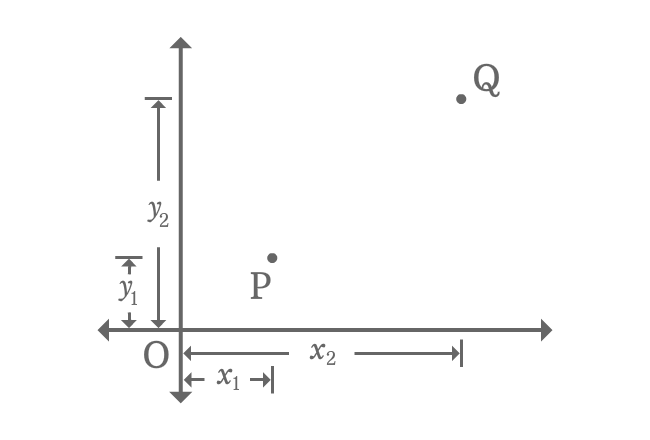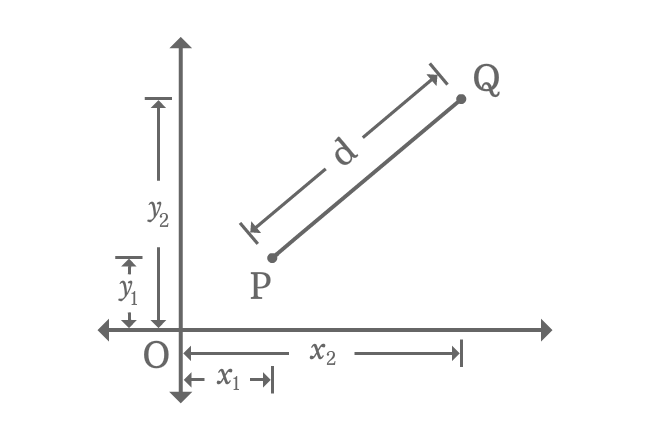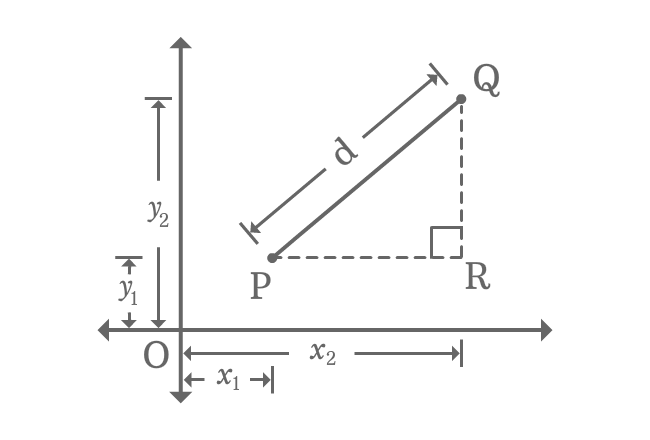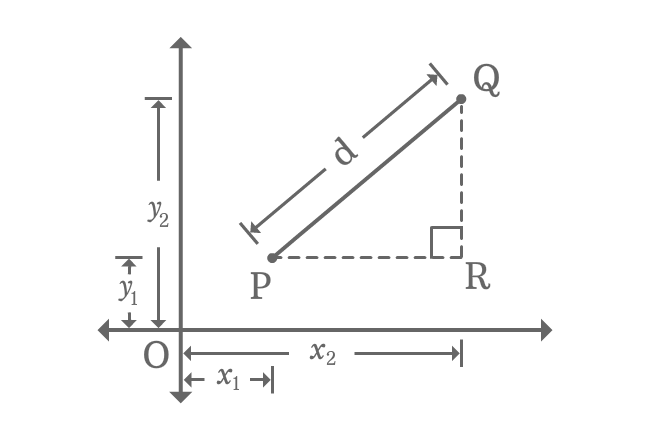
- Draw a parallel line from point $P$ and a perpendicular line from $Q$ towards $x$-axis. The two lines get intersected at point $R$ perpendicularly and form a right triangle, known as $\Delta RPQ$.
Calculate lengths of the sides of triangle
$\overline{PQ}$, $\overline{QR}$ and $\overline{PR}$ are hypotenuse, opposite side (perpendicular) and adjacent side (Base) of right triangle $RPQ$. Now, calculate the length of each side in terms of coordinates of the points.
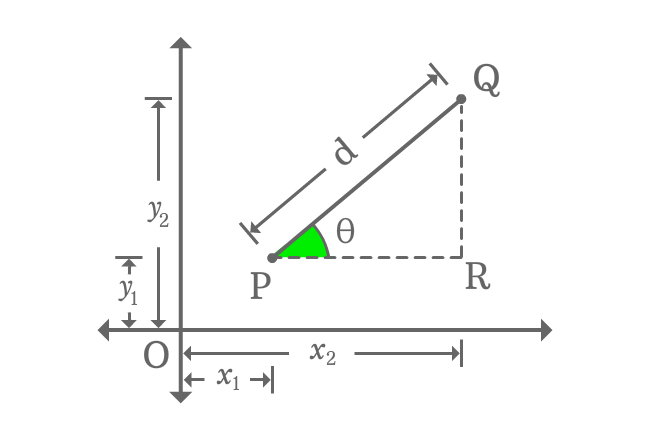
- Length of Opposite side is $QR$ $\,=\,$ $OQ-OR \,=\, y_2-y_1$.
- Length of Adjacent side is $PR$ $\,=\,$ $OR-OP \,=\, x_2-x_1$.
- Length of Hypotenuse is considered as $d$ and it represents the distance between two points. Therefore, $PQ = d$
Use this data to find the distance between any two points in a two dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.
Express relation between sides of triangle
The relation between three sides can be written in mathematical form by Pythagorean Theorem.
${PQ}^2 = {PR}^2+{QR}^2$
Substitute lengths of the all three sides.
$\implies d^2 = {(x_2-x_1)}^2+{(y_2-y_1)}^2$
$\implies d = \pm \sqrt{{(x_2-x_1)}^2+{(y_2-y_1)}^2}$
The distance is a positive factor physically.
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, d = \sqrt{{(x_2-x_1)}^2+{(y_2-y_1)}^2}$
It is called distance formula and used to find distance between any points in a plane. The distance formula reveals that the distance between any two points in a plane is equal to square root of sum of squares of differences of the coordinates.
