The cos of zero degrees is equal to one as per trigonometric mathematics.
$\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, 1$
The cosine of angle zero degrees can be derived in three mathematical approaches but two methods are related to geometric system and the remaining one is related to trigonometry.
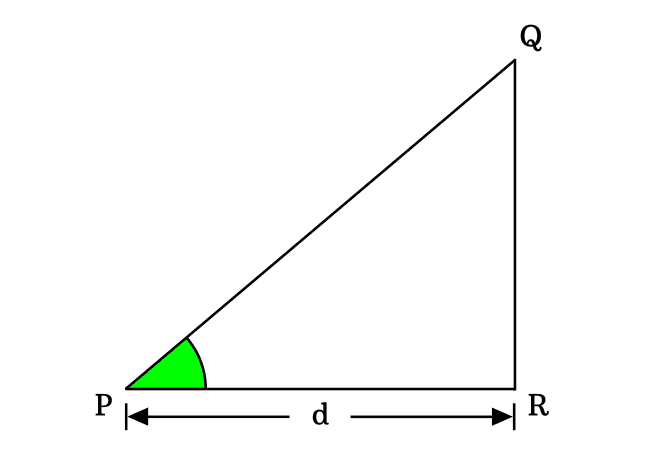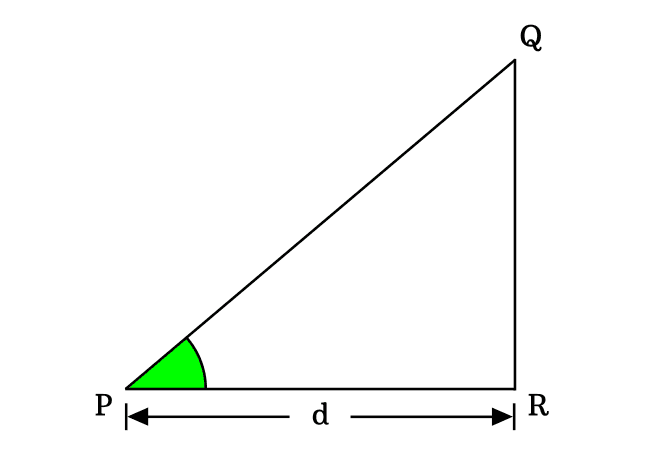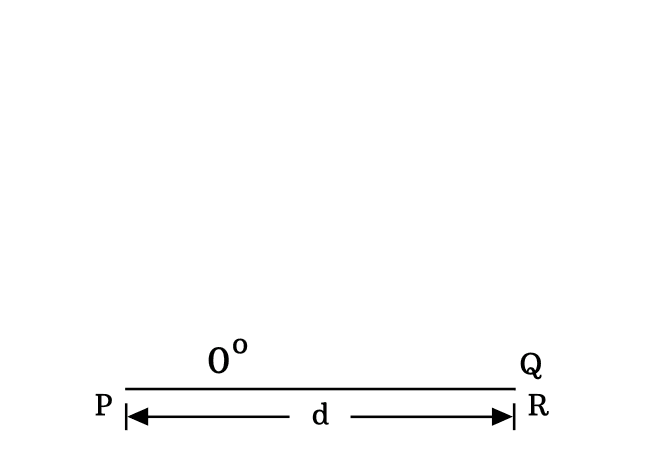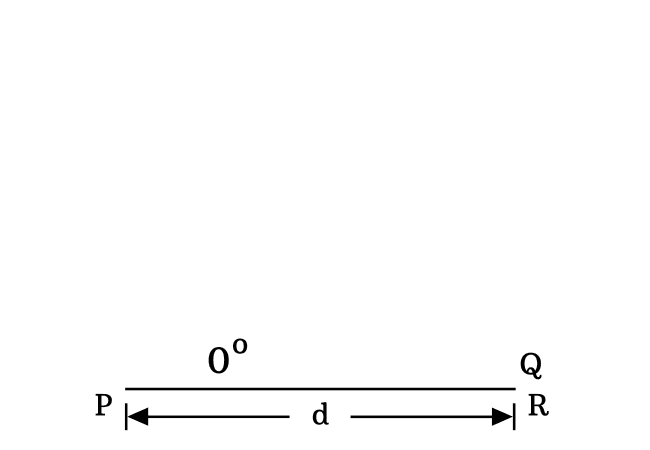
In this method, we consider a property between sides of a triangle for proving the exact value of cosine of angle zero degrees. So, let’s imagine a right triangle with zero degrees angle. Here, $\Delta QPR$ is an example for a right triangle with zero angle.
According to the definition of the cos function, express it in ratio form in terms of lengths of the sides. Actually, the cos function is written as $\cos{(0^°)}$ when the angle of a right triangle is zero radian.
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side}{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}$
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{PR}{PQ}$
In a zero degree right triangle, the lengths of both adjacent side and hypotenuse are equal because the length of the opposite side is equal to zero. Therefore $PQ \,=\, PR$.
$\require{cancel} \implies$ $\cos{(0^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{\cancel{PQ}}{\cancel{PQ}}$
$\,\,\,\therefore\,\,\,\,\,\,$ $\cos{(0^°)}$ $\,=\,$ $1$
The cos of angle zero degrees can also be proved practically by constructing a right triangle with zero degrees angle. It can be done with geometric tools. So, let’s get started to construct a right angled triangle with zero degrees angle.

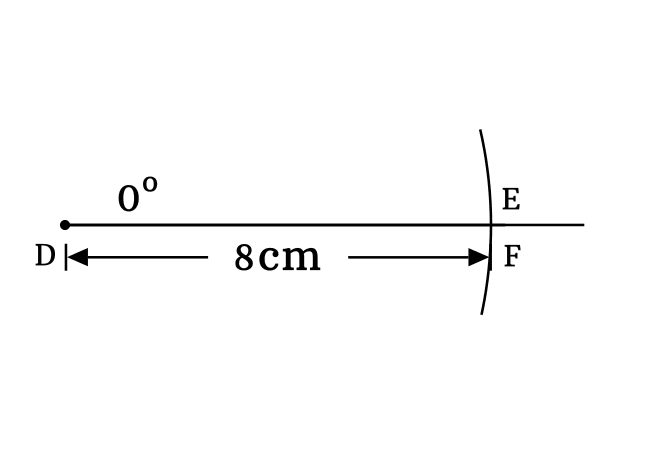
In $\Delta EDF$, the opposite side, adjacent side and hypotenuse are $\overline{EF}$, $\overline{DF}$ and $\overline{DE}$ respectively. $EF = 0\,cm$, $DF = 8\,cm$ and $DE = 8\,cm$. Now, let’s evaluate the cosine of angle zero degrees by the ratio of lengths of its associated sides.
$\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{DF}{DE}$
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{8}{8}$
$\,\,\,\therefore\,\,\,\,\,\,$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, 1$
The cosine of angle zero degrees can also be derived in trigonometry by the fundamentals of trigonometry. According to Pythagorean trigonometric identity, the cos function can be expressed in terms of sine function.
$\cos{\theta} \,=\, \sqrt{1-\sin^2{\theta}}$
In this case, the angle $\theta$ is zero degrees.
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \sqrt{1-\sin^2{(0^°)}}$
We know that the value of sine of zero degrees is equal to zero.
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \sqrt{1-(0)^2}$
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \sqrt{1-0^2}$
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \sqrt{1-0}$
$\implies$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, \sqrt{1}$
$\,\,\,\therefore\,\,\,\,\,\,$ $\cos{(0^°)} \,=\, 1$
These are the possible ways to prove the cos of angle zero degrees in mathematics.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved