What is a Negative Factor?
Fact-checked:
Definition
A non-zero negative integer that divides a given number exactly, without leaving any remainder, is called a negative factor.
Introduction
You have already learned the concept of a factor of a number with non‑zero positive integers. However, a number can also have non‑zero negative integers as factors.
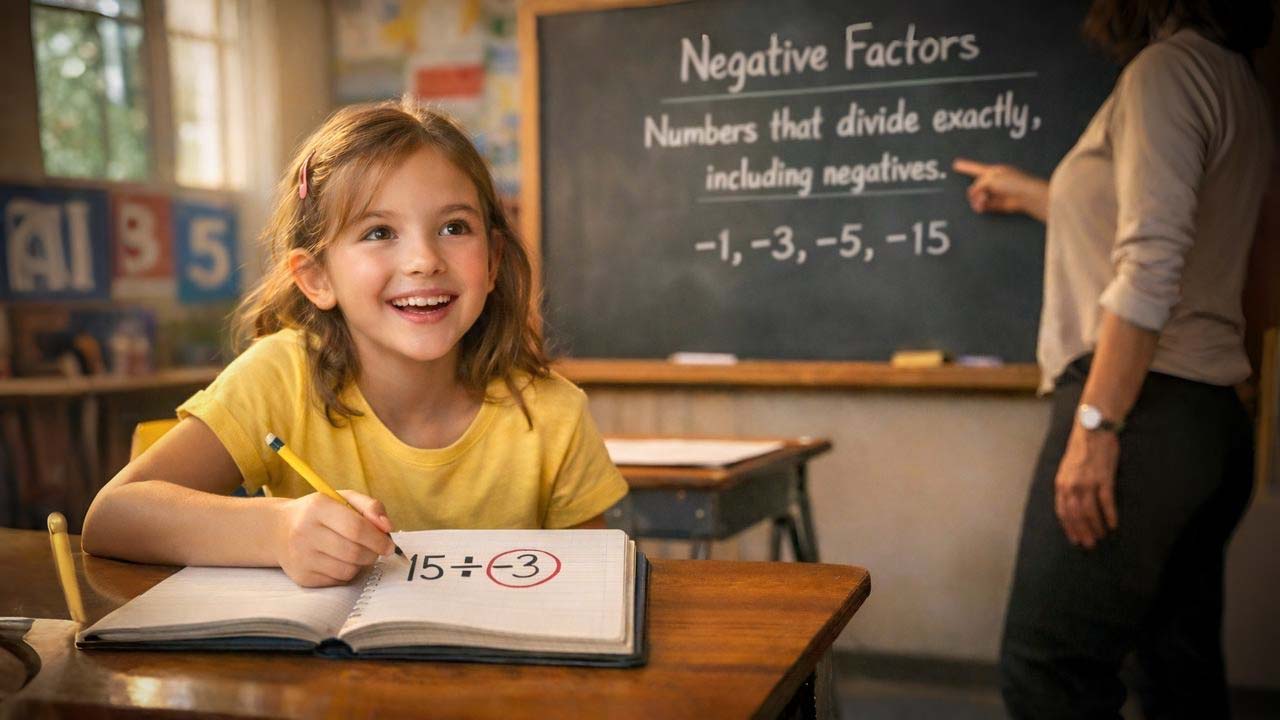
Now you will learn what a negative factor of a number is, its properties including divisibility, and how negative factors relate to each other through simple numerical examples.
Examples of Negative Factors
Let us begin by learning the concept of negative factor in mathematics, with the help of simple numerical examples.
Example
$15 \div (-3)$
The number $−3$ is a negative integer, and $15$ is a whole number and a positive integer. Now, divide $15$ by $−3$ to observe whether there is any remainder.
$\require{enclose}
\begin{array}{rll}
-5 && \hbox{} \\[-3pt]
-3 \enclose{longdiv}{~15}\kern-.2ex \\[-3pt]
\underline{-~~~15} && \longrightarrow && \hbox{$(-3) \times (-5) = 15$} \\[-3pt]
\phantom{00} 0 && \longrightarrow && \hbox{No Remainder}
\end{array}$
When $15$ is divided by $−3$, there is no remainder, which means that $−3$ divides $15$ exactly. Therefore, the negative integer $−3$ is a factor of $15$.
The above arithmetic example shows that a non-zero negative integer that divides a given number exactly, without leaving any remainder, is called a negative factor of that number.
Now, let’s look at another numerical example to understand the concept of a negative factor more clearly.
Example
$15 \div (-5)$
The number $-5$ is a negative integer, and $15$ is a whole number as well as a positive integer. Let’s divide $15$ by $-5$ to see if there is any remainder.
$\require{enclose}
\begin{array}{rll}
-5 && \hbox{} \\[-3pt]
-3 \enclose{longdiv}{~15}\kern-.2ex \\[-3pt]
\underline{-~~~15} && \longrightarrow && \hbox{$(-3) \times (-5) = 15$} \\[-3pt]
\phantom{00} 0 && \longrightarrow && \hbox{No Remainder}
\end{array}$
Dividing $15$ by $-5$ leaves no remainder, which means $-5$ divides $15$ exactly. So, $-5$ is a negative factor of $15$.
These two simple arithmetic examples illustrate the divisibility of numbers and show how to find all negative factors of a number, helping beginners understand what a negative factor is and how it works in mathematics.
These two examples show that $-3$ and $-5$ are negative factors of $15$. When we multiply them, we get the positive number $15$, which shows how negative factors are related to each other.
Example
$(-3) \times (-5) \,=\, 15$
Negative factors of a number are related because some of them can be multiplied to get the original number. This helps beginners understand how negative factors work in mathematics.
Finally, let’s see one more simple example to make it easier to understand negative factors in mathematics.
Example
$15 \div (-4)$
The number $-4$ is a negative integer, and $15$ is a whole number as well as a positive integer. Let’s divide $15$ by $-4$ to check for any remainder.
$\require{enclose}
\begin{array}{rll}
-3 && \hbox{} \\[-3pt]
-4 \enclose{longdiv}{~15}\kern-.2ex \\[-3pt]
\underline{-~~~12} && \longrightarrow && \hbox{$(-4) \times (-3) = 12$} \\[-3pt]
\phantom{00} 3 && \longrightarrow && \hbox{Remainder}
\end{array}$
When $15$ is divided by $-4$, the remainder is $3$. This means $-4$ does not divide $15$ exactly, so $-4$ is not a negative factor of $15$.
These three examples help you understand what a negative factor of a number is.
Relation between Negative and Positive Factors
Negative factors are closely related to positive factors of a number. For every positive factor of a number, there exists a corresponding negative factor with the same numerical value but an opposite sign.
For example, the positive factors of $15$ are $1$, $3$, $5$, and $15$. The corresponding negative factors are $−1$, $−3$, $−5$, and $−15$.
Note that zero is not a factor of any number because division by zero is not defined in mathematics.
Important Facts About Negative Factors
Let’s look at some important points to remember about negative factors of a number.
- Negative factors are always non-zero integers.
- A number can have more than one negative factor.
- Negative factors show us how numbers are related through division and multiplication.

