In calculus, the words “Approach” and “Tend” are often used while we study the limits. So, let’s learn this basic concept to start learning the limits.
According to English language, the meaning of “Approach” or “Tend” is, come near. Hence, the words “Approach” or “Tend” are used to express “come near” in calculus. In mathematics, it is symbolically represented by a right arrow symbol ($\rightarrow$).
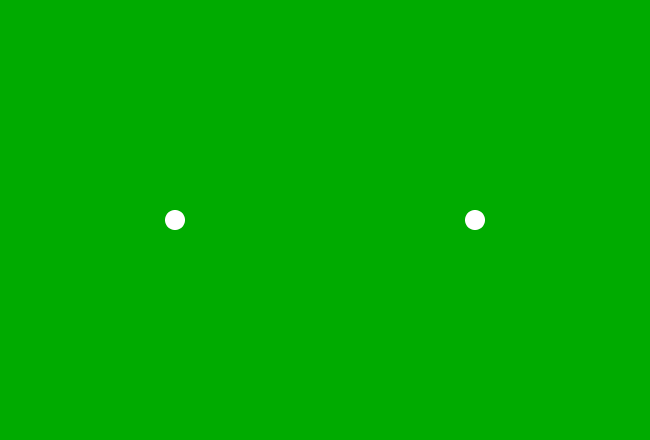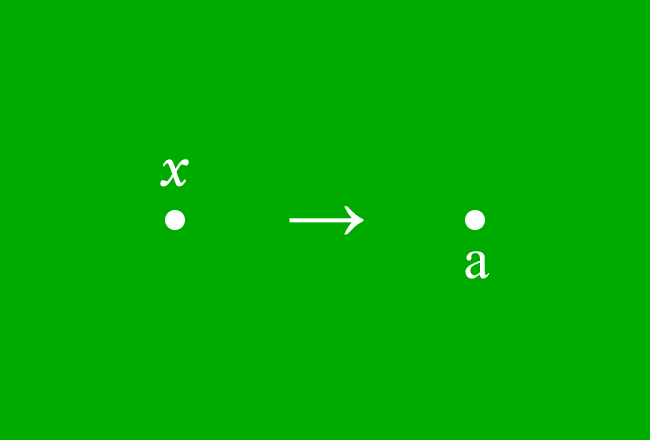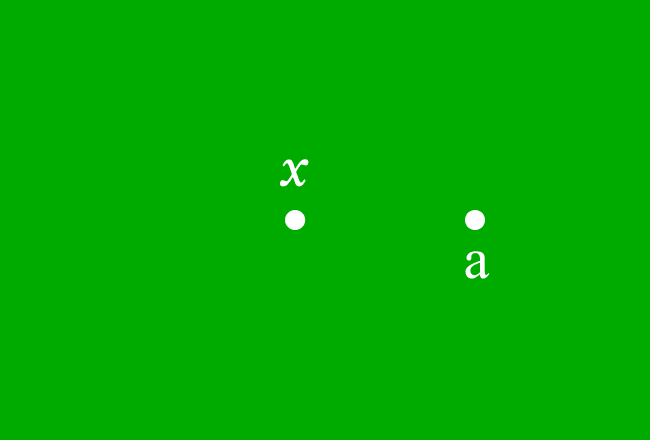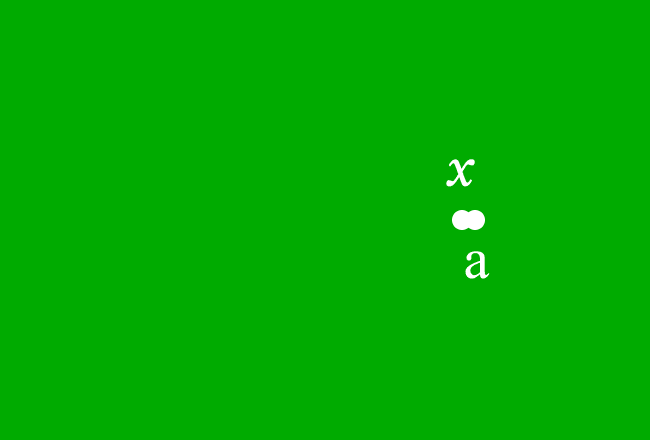
Let $x$ be a variable and $a$ be a constant, and they represent the distances of two points from origin. If the point that appears at $x$ units distance from the origin, comes near to the point that appears at $a$ units distance from the origin, then it’s said that the point at $x$ approaches to the point at $a$.
Mathematically, it is written as $x \,\to\, a$ and it is read in the following three ways.
$x$ is a variable and $a$ is a constant. The value of $x$ starts from $5$ but less than $6$ and the value of $a$ is $6$. Therefore, $x \in [5, 6)$ and $a = 6$.
Take $x = 5$. The values of $x$ and $a$ are not equal because their quantities are not same ($5 \ne 6$). Therefore, $x \ne a$.
Take $x = 5.9$. The value of $5.9$ is not equal to $6$ but its value is closely equal to $6$. In other words, $5.9 \approx 6$. It is expressed in two ways in calculus.
Mathematically, it is written as $5.9 \,\to\, 6$. Therefore, $x \,\to\, a$. Remember, the right arrow represents that the value of $x$ closes the value of $a$ but they’re not equal.
Now, take $x = 5.99$. In this case also, the value of $5.99$ does not equal to $6$ but approximately equals to $6$. Therefore, $5.99 \approx 6$.
Therefore, $x \,\to \, a$ in this case.
The meaning of $x \,\to\, a$ is, the value of $x$ can be anything, which is close to the value of $a$ but not equal to $a$. So, the value of $x$ can be any value closes to $6$, for example $5.9$, $5.95$, $5.991$, $5.999$ and so on.
Let’s study the concept of approach or tend in calculus with some more examples.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved