Cos of negative angle
A mathematical relation of cosine of negative angle with cosine of positive angle is called cosine of negative angle identity.
Formula
$\cos{(-\theta)} \,=\, \cos{\theta}$
Proof
The mathematical relation between cosine of negative angle and cosine of positive angle is derived in mathematical form in trigonometry by geometrical method.
Construction of triangle with positive angle
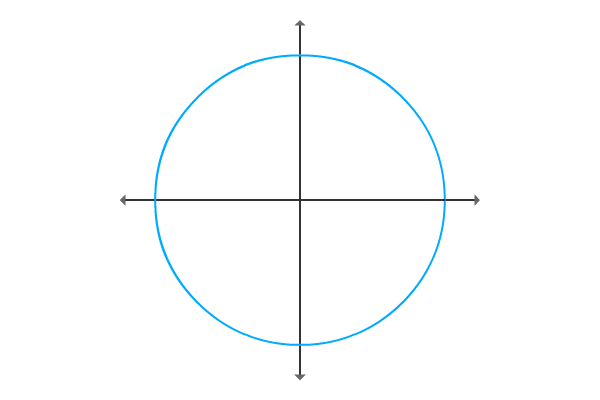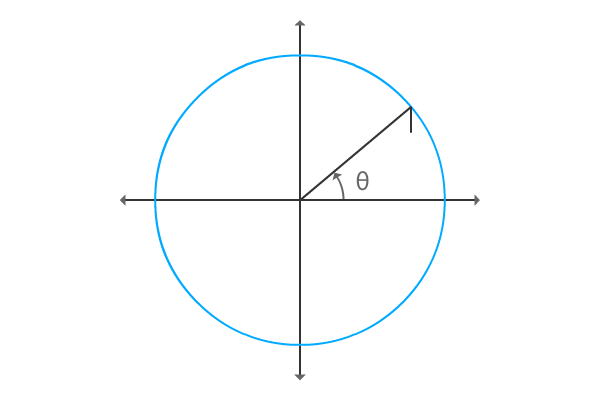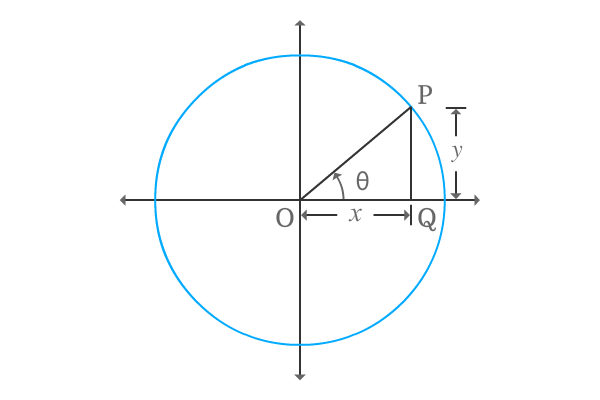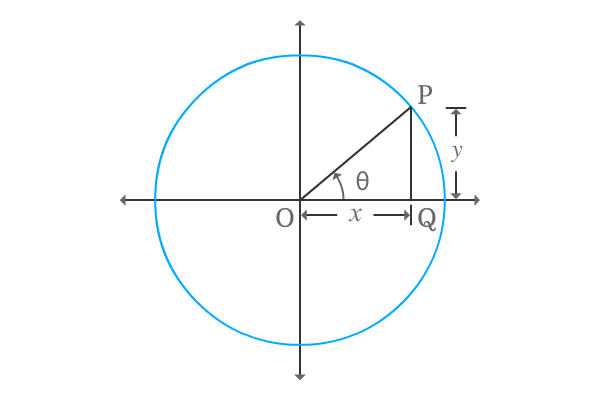
$\Delta QOP$ is a right angled triangle, constructed with an angle theta. Write cosine of angle in terms of ratio of lengths of the sides.
$\cos{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{OQ}{OP}$
$\Delta QOP$ is constructed in first quadrant. So, the lengths of adjacent and opposite sides are positive. Hence, take the lengths of both sides as $x$ and $y$ respectively.
$\implies$ $\cos{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}$
Construction of triangle with negative angle
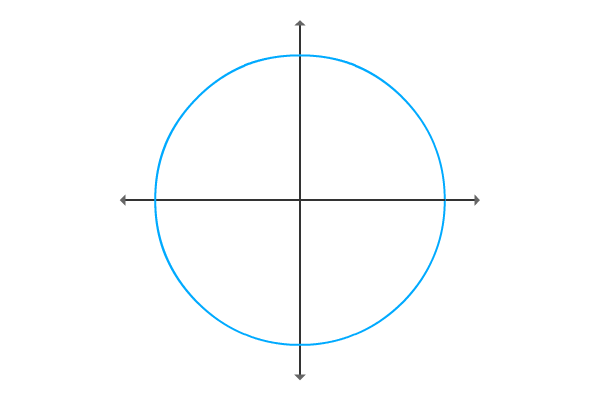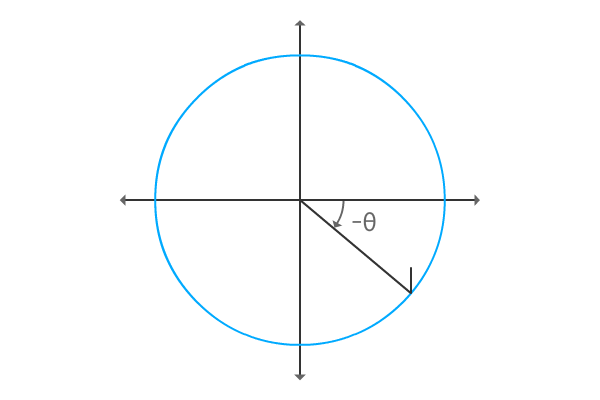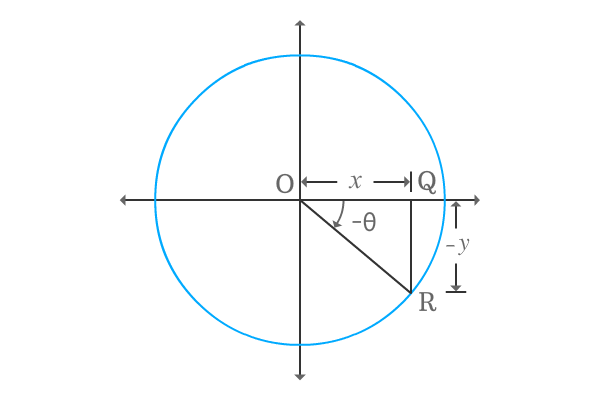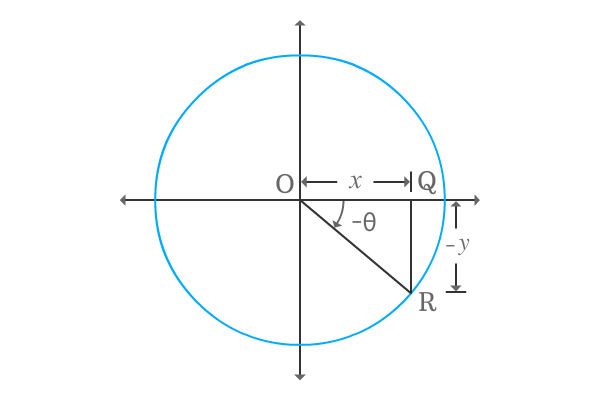
Construct same triangle but with negative angle. So, the angle of the $\Delta ROQ$ will be $–\theta$.
Express, the trigonometric ratio cosine in terms of ratio of the lengths of the associated sides.
$\cos{(-\theta)} \,=\, \dfrac{OQ}{OR}$
In this case, the length of opposite side will be $–y$ but the length of adjacent side is $x$ geometrically.
$\implies$ $\cos{(-\theta)} \,=\, \dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}$
Comparing Cosine functions
Compare equations of both cosine of positive angle and cosine of negative angle.
$\cos{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}$
$\cos{(-\theta)} \,=\, \dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}$
The two equations reveals that cosine of negative angle is always equal to cosine of angle.
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $\cos{(-\theta)} \,=\, \cos{\theta}$
It is called cosine of negative angle identity and often used as a formula in trigonometric mathematics.
