The Pythagorean Theorem is derived in algebraic form by the geometric system. Now, it is your time to know how the square of length of hypotenuse is equal to sum of squares of lengths of opposite and adjacent sides in a right triangle.
$a$, $b$ and $c$ are lengths of sides of a right triangle. $\alpha$ and $\beta$ are two angles and third is a right angle obviously in this triangle. So, let’s study the properties of right triangle before deriving the Pythagorean Theorem in algebraic form.
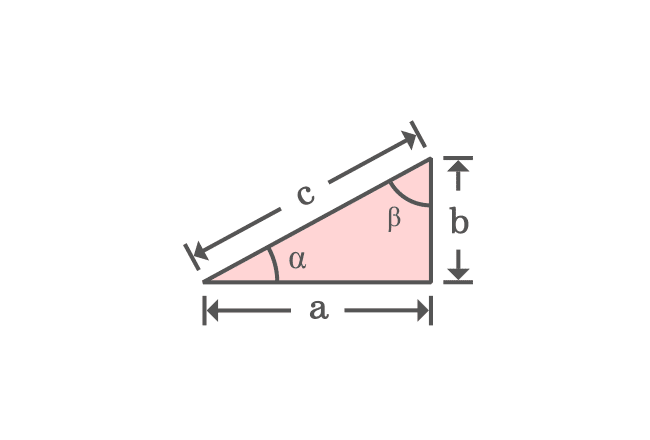
According to sum of angles of a triangle rule, the sum of the interior angles of this triangle is $180^°$.
$\alpha + \beta + 90^°$ $\,=\,$ $180^°$
$\implies$ $\alpha + \beta$ $\,=\,$ $180^°-90^°$
$\implies$ $\alpha + \beta$ $\,=\,$ $90^°$
The equation expresses that the angles $\alpha$ and $\beta$ are complementary angles.
Remember this property and it will be used in deriving the Pythagoras Theorem mathematically.
Take four same right triangles and join the hypotenuses of four right triangles as a closed geometric shape.
It is time to study the geometric shape formed by the joining of the four right triangles.
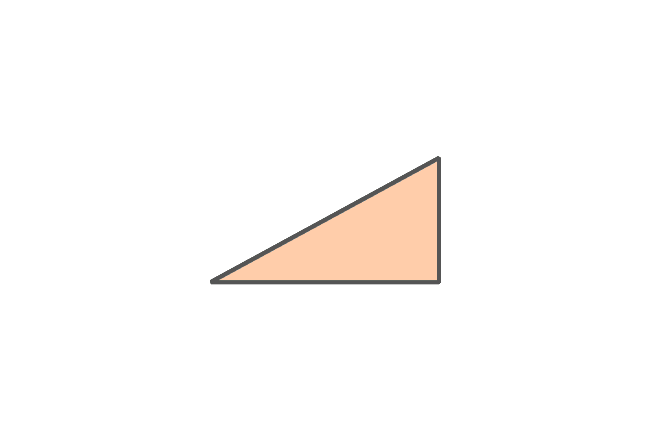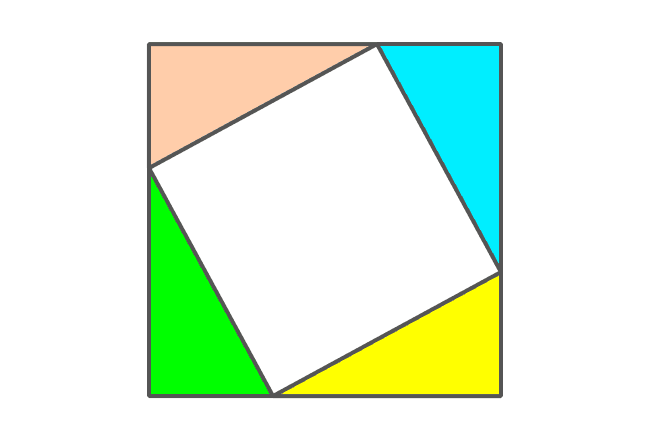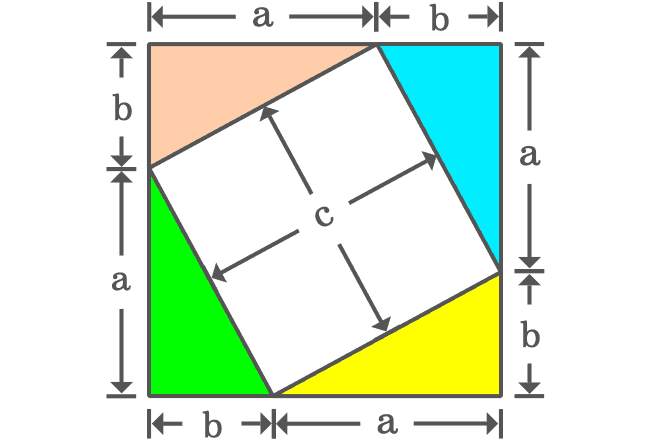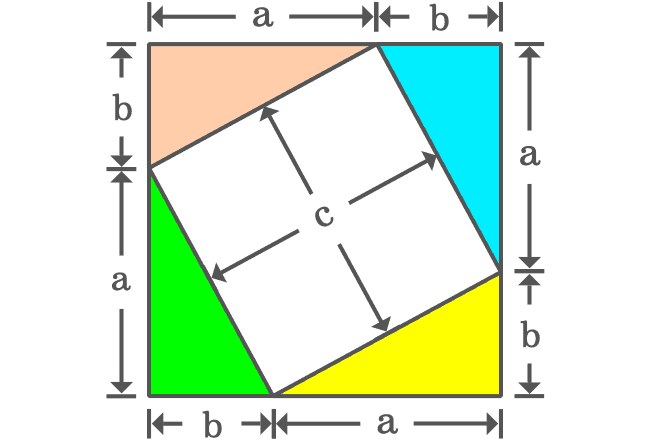
The opposite and adjacent sides of four right triangles form a square externally and the side of the square is $a+b$. Therefore, the area of this square is ${(a+b)}^2$.
The intersection of hypotenuses of four right triangles formed a quadrilateral internally. It is taken that the length of hypotenuse is $c$ and it is also length of the each side of the quadrilateral.
Even though the length of each side of the internal quadrilateral is $c$, we don’t know exactly what kind of quadrilateral it is. It can be determined by finding the angles of this internal quadrilateral.
The angle between any two sides of the internal quadrilateral forms a straight angle with the angles of the two right triangles $\alpha$ and $\beta$. It is also same in the case of other three angles of the quadrilateral. So, four angles of the internal quadrilateral should be equal geometrically and it is taken as $\gamma$.
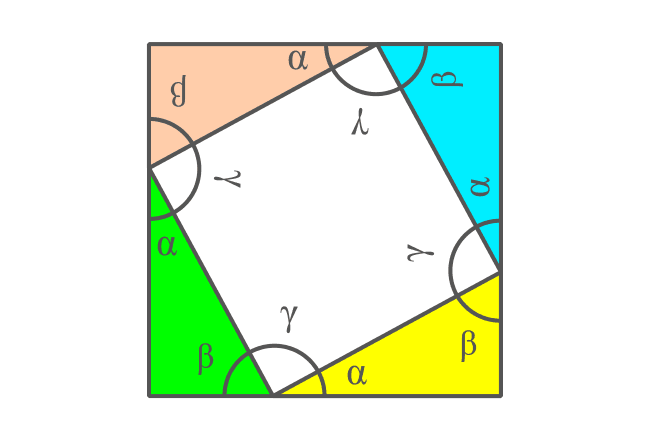
Therefore, the sum of the angles $\alpha$, $\beta$ and $\gamma$ is equal to $180^°$.
$\alpha + \beta + \gamma$ $\,=\,$ $180^°$
It is already proved that $\alpha + \beta$ $\,=\,$ $90^°$ in the previous step.
$\implies$ $90^°+\gamma$ $\,=\,$ $180^°$
$\implies$ $\gamma$ $\,=\,$ $180^°-90^°$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \gamma \,=\, 90^°$
It is proved that the angle $\gamma$ is a right angle and the other three angles are also $90^°$. Therefore, it is proved that the internal quadrilateral is a square.
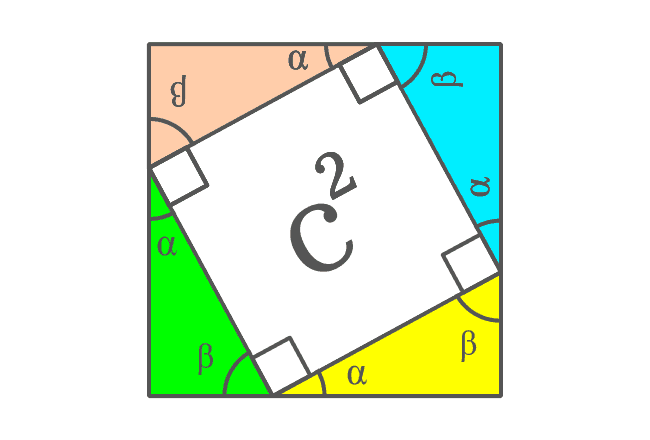
The hypotenuses of all four right triangles are now sides of the square. It is taken that the length of hypotenuse of each right triangle is $c$. So, the length of each side of the square is also $c$ geometrically.
Now, the area of the internal square can be calculated by using area formula of the square.
Therefore, the area of the square is $c \times c$ and it is $c^2$.
Remember the area of this internal square and it will be used in the upcoming step.
A rectangle can be formed by joining hypotenuses of two right triangles. In our case, there are four right triangles which can be added together to form two rectangles.
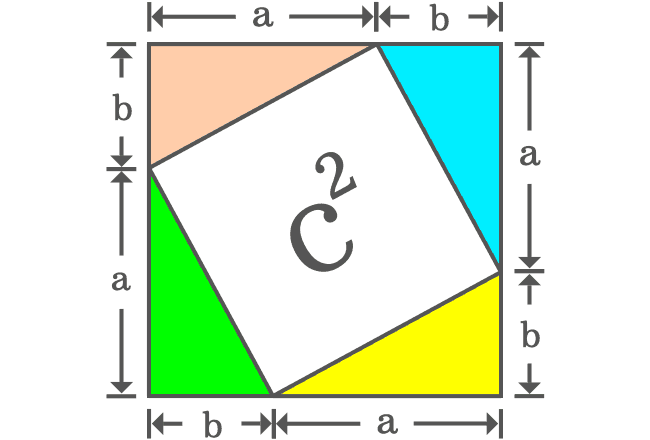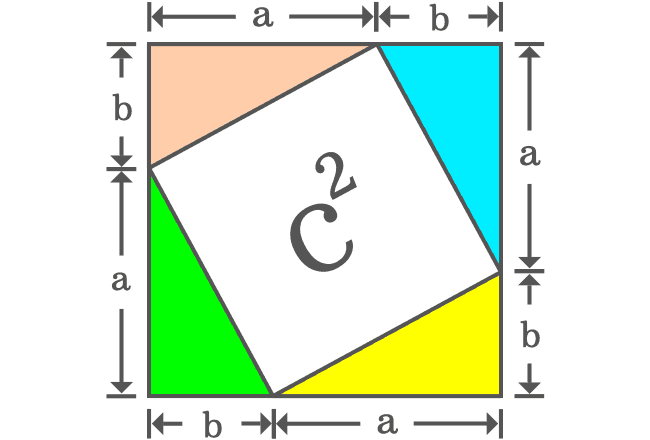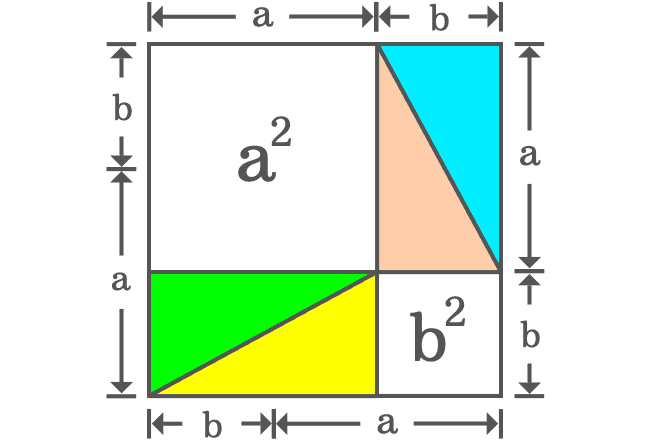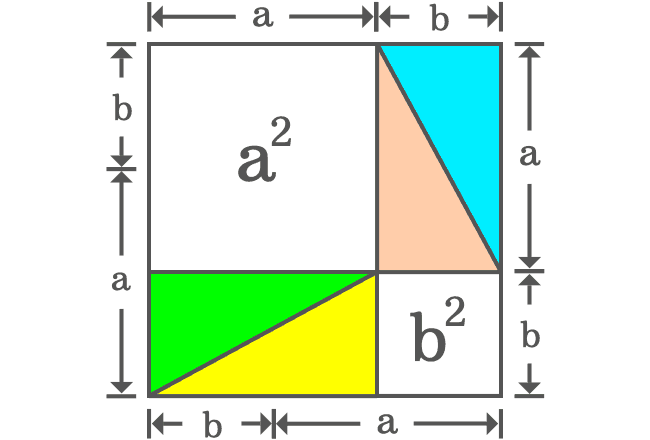
The geometrical arrangement formed two rectangles and two squares. There is no need to find the areas of the rectangles but it is essential to find the areas of the two squares.
The length of each side of the first square is $a$. So, its area is equal to $a^2$. The length of each side of the second square is $b$ and its area is equal to $b^2$. The sum of both squares is equal to $a^2+b^2$.
It can be observed that the square having area of $c^2$ is split as the two squares whose areas are $a^2$ and $b^2$. Therefore, it is geometrically proved that the area of square ($c^2$) is equal to the sum of the areas of two squares.
$\therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $c^2 = a^2+b^2$
Actually, $c$ is length of hypotenuse and, $a$ and $b$ are lengths of adjacent and opposite sides of the right triangle.
Therefore, it is proved that the square of length of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the opposite and adjacent sides of the right triangle.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2023 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved